Select Right Valve from Flow Velocity
2016-10-16
Valve flow and flow-velocity depends mainly on the valve port size, related with resistance imposed by valve structure type,the valve working pressure,medium concentration and other factors also have internal connection with the valve flow and flow-rate.
The valve port size effects the flow and flow-rate,while flow and flow-rate are mutual interdependence, When flow is certain,smaller port size can bring bigger flow velocity,smaller one can realize through making port size bigger;conversely, bigger port size leads to smaller flow velocity,getting higher flow rate by reduce port size.Faster flow rate can reach by reducing port size while it can also bring bigger resistance loss,greater harm on valve. It also may lead static effect to flammable and explosive media and cause dangerous accident;on the other hand,it’s not economic for low efficiency caused by smaller velocity.For viscous and explosive media, a smaller flow rate should be considered. When comes to oil and other big-viscosity liquid,the flow rate should be decided by viscosity,generally take 0.1 ~ 2m/s.
Under normal circumstances, the flow rate is known, the flow rate can be determined empirically. Commonly velocity of different medium are shown in Table2-2 below. Through the flow rate and flow, can calculate the nominal diameter of the valve.
For the same size valve, different structure can bring different flow resistance.Under the same conditions, the
Bigger the resistance coefficient of the valve is, the bigger decrease of flow and flow rate when go thought valve port.Vice versa. Commonly velocity of different medium are shown in TABLE 2-2 below.
Medium Name |
Condition |
Velocity | Medium Name |
Condition |
Velocity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m/s) | (m/s) | ||||
Saturated Vapor |
DN>200 | 30~40 | Acetylene gas |
ρ<0.01 (gage pressure) | 3~4 |
| DN=200~100 | 25~35 | ρ<0.15 (gage pressure) | 4~8 | ||
| DN<100 | 15~30 | ρ<2.5 (gage pressure) | 5 | ||
Superheated steam |
DN>200 | 40~60 | Chlorine |
gas | 10~25 |
| DN=200~100 | 30~50 | fluid | 1.6 | ||
| DN<100 | 20~40 | Hydrogen chloride | gas | 20 | |
| Low pressure steam | ρ<1.0 (absolute pressure) | 15~20 | Liquid ammonia |
vaccum | 0.05~0.3 |
| Medium pressure steam | Ρ=1.0~4.0 (absolute pressure) | 20~40 | Ρ≤0.6 (gage pressure) | 0.3~0.8 | |
| High pressure steam | Ρ=4.0~12.0 (absolute pressure) | 40~60 | Ρ≤2.0 (gage pressure) ) | 0.8~1.5 | |
Compressed gas |
vaccum | 5~10 | Sodium hydroxide |
concentration 0~30% | 2 |
| Ρ≤0.3 (gage pressure) | 8~12 | concentration 30%~505 | 1.5 | ||
| Ρ=0.3~0.6 (gage pressure) | 10~20 | concentration 50%~73% | 1.2 | ||
| Ρ=0.6~1.0 (gage pressure) | 10~15 | Sulfuric acid |
concentration 88%~93% | 1.2 | |
| Ρ=1.0~2.0 (gage pressure) | 8~12 | concentration 93%~100% | 1.2 | ||
| Ρ=2.0~3.0 (gage pressure) | 3~6 | Hydrochloric acid | 1.5 | ||
| Ρ=3.0~30.0 (gage pressure) | 0.5~3 | Water and viscosity similar to the liquid |
Ρ=0.1~0.3 (gage pressure) | 0.5~2 | |
Oxygen gas |
Ρ=0~0.05 (gage pressure) | 5~10 | Ρ≤1.0 (gage pressure) | 0.5~3 | |
| Ρ=0.05~0.6 (gage pressure) | 7~8 | Ρ≤8.0 (gage pressure) | 2~3 | ||
| Ρ=0.6~1.0 (gage pressure) | 4~6 | Ρ≤20~30 (gage pressure) | 2~3.5 | ||
| Ρ=1.0~2.0 (gage pressure) | 4~5 | heat-supply circulating water,cooling water | 0.3~1 | ||
| Ρ=2.0~3.0 (gage pressure) | 3~4 | pressure backwater | 0.5~2 | ||
| Coal gas | 2.5~15 | non-pressure backwater | 0.5~1.2 | ||
| Semi - water gas | Ρ=0.1~0.15 (gage pressure) | 10~15 | Water supply |
main pipe Ρ=0.3 (gage pressure) | 1.5~3.5 |
| Natural gas | 30 | branch pipe Ρ=0.3 (gage pressure) | 1~1.5 | ||
| Nitrogen | Ρ=5~10 (absolute pressure) | 15~25 | Boiler water supply | >3 | |
Ammonia gas |
vaccum | 15~25 | Steam condensate | 0.5~1.5 | |
| Ρ<0.3 (gage pressure) | 8~15 | Condensate | flow automatically | 0.2~0.5 | |
| Ρ<0.6 (gage pressure) | 10~20 | Superheated water | 2 | ||
| Ρ≤2 (gage pressure) | 3~8 | Seawater, slightly alkaline water | Ρ<0.6 (gage pressure) | 1.5~2.5 | |
| Note:unit of DN is mm;unit of P is Mpa | |||||
Table 2-2 Flow Velocity of Common Different Mediums
1-Butterfly valve,its resistance coefficient is small, within 0.5
2-Ball valve,smallest resistance coefficient,about 0.1
3-Gate valve,small resistance coefficient,range from 0.1 to 1.5;big size (0.2 ~ 0.5),reduced port gate valve has a little bigger resistance coefficient
4-Globe valve,big resistance coefficient,from 4 to 7,Y pattern globe valve has smallest resistance coefficient, 1.5 ~ 2,forged type has biggest one,even can reach 8
5-Check valve,varied upon different structure,swing type has big resistance coefficient,lift type has the biggest one (12).
6-Plug valve,with small resistance coefficient,about 0.4 ~ 1.2
Note: the valve resistance coefficient above are basing on full-open status.
Valve diameter selection, should take machining accuracy ,size deviation and others into account ,also reserve certain overmeasure (generally 15%),in actual application, it’s decided by size of pipeline diameter.
Attachment:
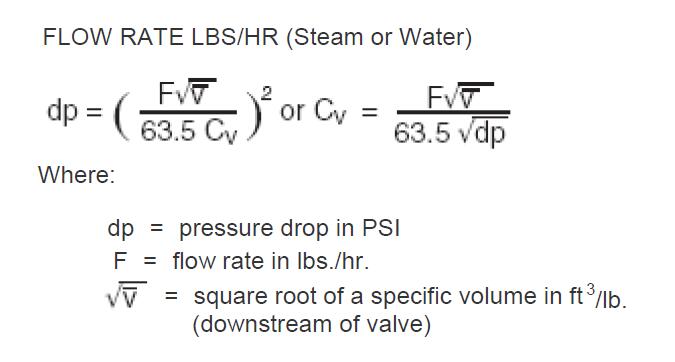
Valve coefficient (Cv) is a number which represents a valve’s ability to pass flow. The bigger the Cv, the more flow a valve can pass with a given pressure drop. A Cv of 1 means a valve will pass 1 gallon per minute (gpm) of 60oF water with a pressure drop (dp) of 1 PSI across the valve. A Cv of 350 means a valve will pass 350 gpm of 60oF water with a dp of 1 PSI